ProQuad as the 2nd MMRV Dose: Clinical data on febrile seizures
Get the facts about the risk of febrile seizures after the second dose of ProQuad® (Measles, Mumps, Rubella and Varicella Virus Vaccine Live)
MMRV series completion with ProQuad
Since 2010, the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices generally preferred combination MMRV for second dose vaccination against measles, mumps, rubella, and varicella.
Learn more about the data
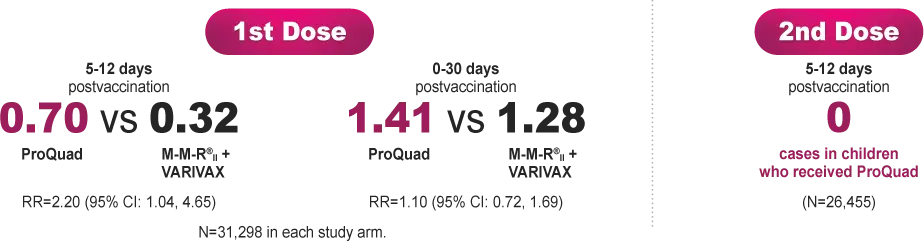
Incidence of febrile seizure with ProQuad vs M-M-R®II (Measles, Mumps, and Rubella Virus Vaccine Live) + VARIVAX® (Varicella Virus Vaccine Live) per 1000 children 12 months to 60 months of age.

Administration of ProQuad (dose 1) to children 12 to 23 months old who have not been previously vaccinated against measles, mumps, rubella, or varicella, nor had a history of the wild-type infections, is associated with higher rates of fever and febrile seizures at 5 to 12 days after vaccination when compared to children vaccinated with dose 1 of both M-M-R®II and VARIVAX administered separately.
Study design
Safety was evaluated in an observational study that included 69,237 children aged 12 months to 12 years vaccinated with ProQuad after a 1st dose with M-M-R®II + VARIVAX. A historical comparison group included 69,237 age-, gender-, and date-of-vaccination (day and month) matched subjects who were given M-M-R®II and VARIVAX concomitantly. The primary objective was to assess the incidence of febrile seizures occurring within various time intervals after vaccination in 12- to 60-month-old children who had neither been vaccinated against measles, mumps, rubella, or varicella, nor had a history of the wild-type infections (N=31,298 vaccinated with ProQuad, including 31,043 who were 12 to 23 months old). The incidence of febrile seizures was also assessed in a historical control group of children who had received their first vaccination with M-M-R®II and VARIVAX concomitantly (N=31,298, including 31,019 who were 12 to 23 months old). The secondary objective was to assess the general safety of ProQuad in the 30-day period after vaccination in children 12 months to 12 years old.


